Firehose #183: 😬 Legacy of a "crazy" deal. 😬
How Yuri Milner's Facebook investment catalyzed a decade of "private IPOs," and how public market investors finally caught up.
Update
Hello, all.
After a few months’ break, I’m back to my weekly writing habit. I will try to stay on track this time. I’m admittedly a bit rusty, so please forgive verbosity, typos, etc while I’m getting back into my rhythm.
This week’s Firehose will just feature the “One Big Thought.” I need to collect enough material for the other sections, so give me a few weeks to do that. I also plan on adding a new #climate section to reflect an increasing interest of mine.
For now, enjoy! Excited to return to your inbox.
One Big Thought
Private markets have been more bullish on tech than public markets for most of my career in VC.
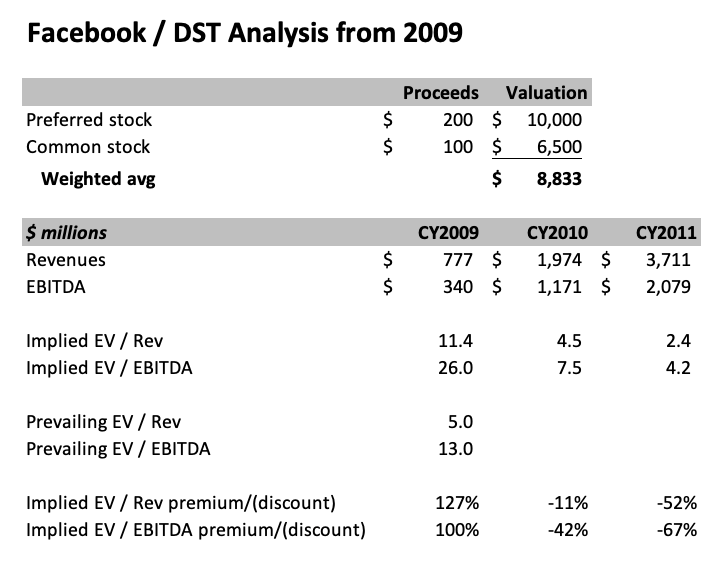
In May 2009 (my first month on the job), the news leaked that Facebook* was raising $200M from an obscure Russian investment group called DST at a whopping $10B valuation. A few months later, DST initiated a tender offer for another $100M of Facebook common stock at a $6.5B valuation.
While few in the industry knew of Facebook’s incredible numbers at the time, the chatter was highly skeptical. But, DST’s Yuri Milner was confident in this Techcrunch interview with Mike Arrington at the time:
MA: Why did you invest in Facebook?
YM: Because it’s a great business.
MA: You’re comfortable with the $10B valuation?
YM: Absolutely. And, you know, I can repeat the reasons why. Basically, I think they have a very unique perspective on social network monetization, that other investors don’t necessarily see. You see how social networks have been monetized in our part of the world, and we’re just doing our math and coming up with numbers that we feel very comfortable with going forward. We don’t really value this business on (fee?) basis 2009 but rather on a longer term, based again on our experience, and we’re very confident that, you know, those numbers can be achieved.
Of course, history proved Yuri’s investment to be prescient. He had seen global social networks monetize and realized that Facebook’s ARPU should be bigger given American’s size and GDP per capita. He also saw Facebook’s engagement numbers in the US and was able to make assumptions around potential ad volume in the network. In short, his experience from other parts of the world was portable and allowed him to see a bit farther into the future than most other investors at the time.
In its S-1 filing, Facebook ended up disclosing $777M of revenue in 2009, with incredible 185% YoY growth. EBITDA was $340M. The blended cost of Yuri’s $200M preferred shares (at $10B) and his $100M common shares (at $6.5B) was $8.8B. Yuri’s entry multiples were therefore 11x 2009 revenues and 26x 2009 EBITDA. Facebook continued to grow rapidly in the following years — to $2.0B revenues and $1.2B EBITDA in 2010, and $3.7B revenues and $2.1B EBITDA in 2011.
At the time, Facebook listed the following companies on its list of competitors:
Amazon.com; Apple; Cisco Systems; eBay; Google; LinkedIn; Microsoft; Netflix; Oracle; salesforce.com; VMware; Yahoo!; and Zynga.
Here’s what (most of) that group’s trailing revenue multiples looked like, both historically through 2011, with the May 2009 deal announcement highlighted below:
Google hadn’t traded north of a 10x trailing multiple since the early 2000’s. At the time of the DST deal, the top comps (Google, VMWare) were both trading at half of Yuri’s multiple. The EBITDA multiple chart below is messier, but shows a range of 6.5-40x, with the median closer to 10-15x (Google at 13x), and a few outliers like Amazon and VWMare at the top of the range. Yuri’s deal wasn’t priced at the top of the market on an EBITDA basis, but its EBITDA multiple was notably 2x Google’s.
In summary, Yuri bought Facebook at 2x+ the revenue and EBITDA multiples of its nearest competitor (Google) and at a broad premium to the market. However, Facebook handily beat the market on both growth and profitability. With respect to the former, its top comps above grew at 30-40% CAGR in 2009, as shown below:
Because Facebook was growing 4-5x faster than its market comps, what began as a 100% premium on the stock vs market multiples turned into a 50-70% discount in just a few years:
Fundamentally, this is the math that made Yuri’s growth investment in Facebook such a legendary move. Based on his past experience investing globally, he saw that Facebook’s potential growth was so much greater than any other US internet company at that moment in time. He could have paid up to double his blended cost and still have been “in the money” by 2011.
After the Facebook IPO validated the DST investment, a flood of private growth stage capital entered the tech markets. Mark Suster of Upfront Ventures published a post that showed $100+ million rounds grew from 13% of financings in 2013 to 47% in 2018. These so-called “mega rounds” became the “private IPO” of the day, allowing companies to push out their actual IPOs by many years. 2015 was the first year when more mega-rounds occurred than traditional IPOs:
While these private growth investors gained increasing conviction to pay higher multiples for market leading technology companies, the public markets demurred. According to Meritech’s Alex Clayton, other than a brief spike in the 2013 time frame, median NTM revenue multiples for SaaS businesses hovered around 7-8x fairly consistently from 2011-19:
My own recollection is that high quality, private SaaS companies regularly traded at 8-10x ARR for a good portion of the last 5 years. Since COVID’s acceleration of the software market in 2020-2021, we now regularly see significantly higher private multiples. Some companies are even raising at 100x ARR:

Even so, public markets today are often valuing tech companies more aggressively than private investors. We can see this development in part by looking at the dispersion between public and private valuations within a given sector (see below for SaaS). An analysis by SaaS Capital shows that the dispersion is growing, driven by a handful of superb performers accelerated by COVID tailwinds:
Adding to the public market’s enthusiasm is the SPAC surge of 2020. According to Bloomberg, SPACs raised nearly $26 billion in January 2021 alone. This capital will compete to bid up prices on the best assets, and maybe some of the mediocre ones as well:
The surge in valuations definitely makes an investor’s job harder. You can’t simply “get lucky” by investing below the market price. Market timing is working against you.
That’s why I go back to Yuri’s insight in 2009 as an inspiration. He had a simple insight, informed by his own experience (“You see how social networks have been monetized in our part of the world, and we’re just doing our math and coming up with numbers that we feel very comfortable with going forward.”) in a market that few appreciated at the time. He was willing to pay a significant premium (100%+ vs. market comps) based on that insight because he was confident that future growth would be multiples of the slower growing comp set.
Even in today’s “crazy” market environment, I still believe this analysis works for the right companies. Plenty of deals that look crazy today won’t in retrospect.
Enjoyed this newsletter?
Getting Drinking from the Firehose in your inbox via Substack is easy. Click below to subscribe:
Have some thoughts? Leave me a comment:
Or share this post on social media to get the word out:
Disclaimer: * indicates a Lightspeed portfolio company, or other company in which I have economic interest. I also have economic interest in AAPL, ADBE, AMT, AMZN, BABA, BRK, BLK, CCI, GOOG/GOOGL, FB, HD, LMT, MA, MCD, MSFT, NSRGY, NEE, PYPL, SHOP, SNAP, SPOT, SQ, TMO, TWLO, VEEV, and V. I own some BTC as well.